CLI Configuration
Use the atmos.yaml configuration file to control the behavior of the atmos CLI
Everything in the atmos CLI is configurable. The defaults are established in the atmos.yaml configuration file. The CLI configuration should not
be confused with Stack configurations, which have a different schema.
Think of this file as where you bootstrap the settings or configuration of your project. If you'll be using
terraform, then this is where
you'd specify the command to run (e.g. opentofu),
the base path location of the components, and so forth.
Configuration File (atmos.yaml)
The CLI config is loaded from the following locations (from lowest to highest priority):
- System directory (
/usr/local/etc/atmos/atmos.yamlon Linux,%LOCALAPPDATA%/atmos/atmos.yamlon Windows) - Home directory (
~/.atmos/atmos.yaml) - Current directory (
./atmos.yaml) - Environment variable
ATMOS_CLI_CONFIG_PATH(the ENV var should point to a folder without specifying the file name)
Each configuration file discovered is deep-merged with the preceding configurations.
Atmos supports POSIX-style greedy Globs for all file
names/paths (double-star/globstar ** is supported as well)
Default CLI Configuration
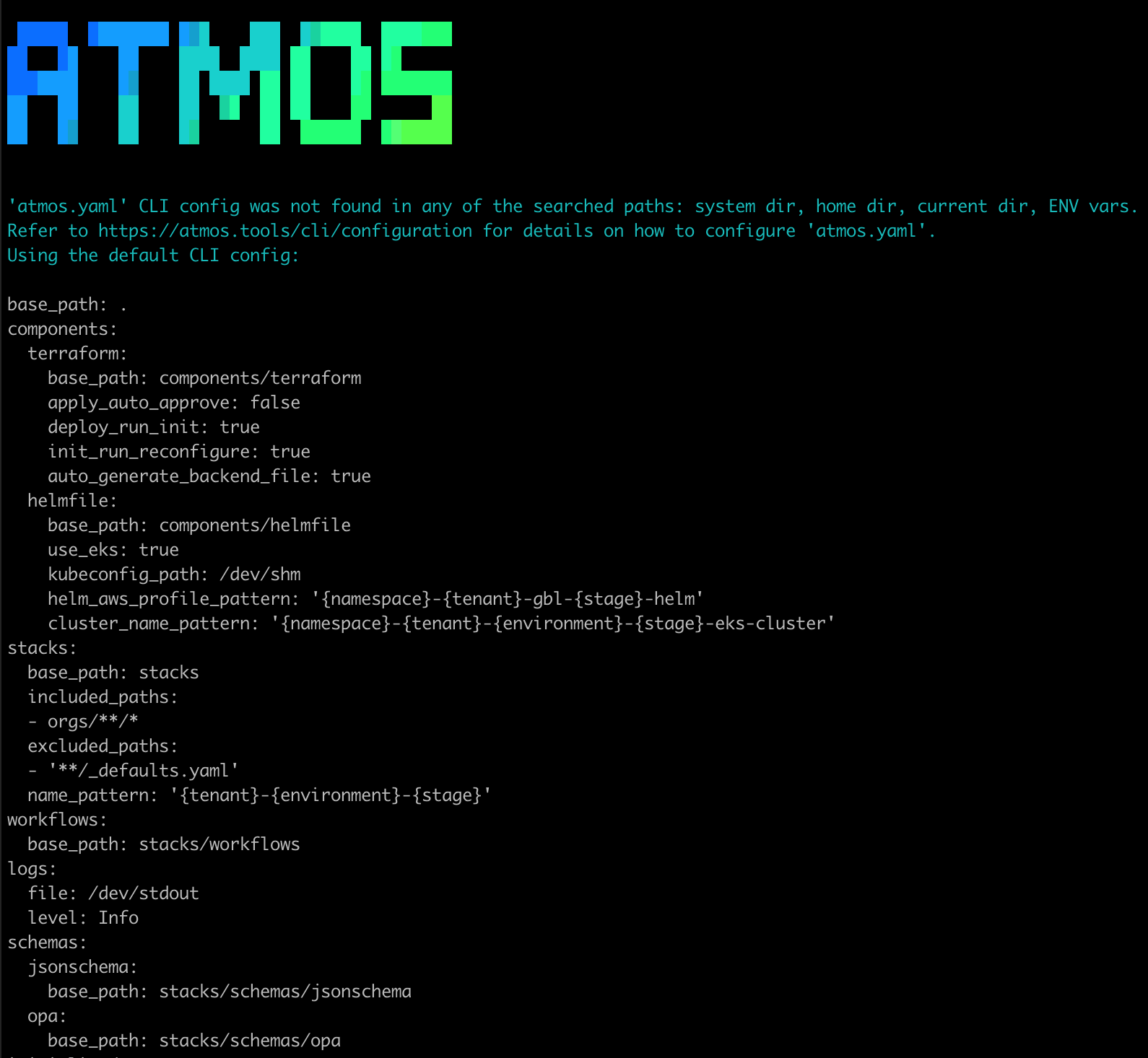
If atmos.yaml is not found in any of the searched locations, Atmos will use the following default CLI configuration:
atmos.yaml
If Atmos does not find an atmos.yaml file and the default CLI config is used, and if you set the ENV variable ATMOS_LOGS_LEVEL to Debug
(e.g. export ATMOS_LOGS_LEVEL=Debug) before executing Atmos commands, you'll see the following message:
What follows are all the sections of the atmos.yaml configuration file.
Base Path
The base path for components, stacks, workflows and validation configurations.
It can also be set using ATMOS_BASE_PATH environment variable, or by passing the --base-path command-line argument.
It supports both absolute and relative paths.
If not provided or is an empty string, components.terraform.base_path, components.helmfile.base_path, stacks.base_path and workflows.base_path
are independent settings (supporting both absolute and relative paths).
If base_path is provided, components.terraform.base_path, components.helmfile.base_path, stacks.base_path, workflows.base_path,
schemas.jsonschema.base_path and schemas.opa.base_path are considered paths relative to base_path.
base_path: "."
Settings
The settings section configures Atmos global settings.
atmos.yaml
settings.list_merge_strategySpecifies how lists are merged in Atmos stack manifests.
The following strategies are supported:
replace- Most recent list imported wins (the default behavior).
append- The sequence of lists is appended in the same order as imports.
merge- The items in the destination list are deep-merged with the items in the source list. The items in the source list take precedence. The items are processed starting from the first up to the length of the source list (the remaining items are not processed). If the source and destination lists have the same length, all items in the destination lists are deep-merged with all items in the source list.
Workflows
atmos.yaml
Integrations
Atmos supports many native Atmos integrations. They extend the core functionality of Atmos.
atmos.yaml
For more information, refer to Atmos Integrations.
Schemas
Configure the paths where to find OPA and JSON Schema files to validate Atmos stack manifests and components.
atmos.yaml
For more information, refer to:
Logs
Logs are configured in the logs section:
atmos.yaml
-
logs.file- the file to write Atmos logs to. Logs can be written to any file or any standard file descriptor, including/dev/stdout,/dev/stderrand/dev/null. If omitted,/dev/stdoutwill be used. The environment variableATMOS_LOGS_FILEcan also be used to specify the log file -
logs.level- Log level. Supported log levels areTrace,Debug,Info,Warning,Off. If the log level is set toOff, Atmos will not log any messages (note that this does not prevent other tools like Terraform from logging). The environment variableATMOS_LOGS_LEVELcan also be used to specify the log level
To prevent Atmos from logging any messages (except for the outputs of the executed commands), you can do one of the following:
-
Set
logs.fileor the ENV variableATMOS_LOGS_FILEto/dev/null -
Set
logs.levelor the ENV variableATMOS_LOGS_LEVELtoOff
Note that when you set the log level to Debug or Trace, Atmos will log additional messages before printing the output
of an executed command. For example, let's consider the atmos describe affected command:
atmos.yaml
With logs.level: Trace, and logs.file: "/dev/stdout", all the messages and the command's JSON output will be printed
to the console to the /dev/stdout standard output.
This behavior might be undesirable when you execute the command atmos describe affected in CI/CD (e.g. GitHub Actions).
For example, you might want to log all the Atmos messages (by setting logs.level: Trace) for debugging purposes,
and also want to parse the JSON output of the command (e.g. by using jq) for further processing. In this case, jq
will not be able to parse the JSON output because all the other messages make the output an invalid JSON document.
To deal with that, you can set logs.file to /dev/stderr in atmos.yaml:
atmos.yaml
Now when the atmos describe affected command is executed, the additional messages are printed to /dev/stderr,
but the command's JSON output is printed to /dev/stdout, allowing jq to parse it without errors.
Aliases
CLI command aliases are configured in the aliases section.
An alias lets you create a shortcut name for an existing CLI command. Any CLI command can be aliased, including the Atmos
native commands like terraform apply or describe stacks, as well as Atmos Custom Commands.
For example:
atmos.yaml
Execute an alias as you would any Atmos native or custom command:
The aliases configured in the aliases section automatically appear in Atmos help, and are shown as
alias for '<command>'.
For example:
An alias automatically supports all command line arguments and flags that the aliased command accepts.
For example:
atmos up <component> -s <stack>supports all the parameters from the aliased commandatmos terraform apply <component> -s <stack>atmos dc <component> -s <stack>supports all the parameters from the aliased commandatmos describe component <component> -s <stack>
Templates
Atmos supports Go templates in stack manifests.
Sprig Functions, Gomplate Functions and Gomplate Datasources are supported as well.
For more details, refer to Atmos Stack Manifest Templating
atmos.yaml
-
templates.settings.enabled- a boolean flag to enable/disable the processing ofGotemplates in Atmos stack manifests. If set tofalse, Atmos will not processGotemplates in stack manifests -
templates.settings.sprig.enabled- a boolean flag to enable/disable the Sprig Functions in Atmos stack manifests -
templates.settings.gomplate.enabled- a boolean flag to enable/disable the Gomplate Functions and Gomplate Datasources in Atmos stack manifests -
templates.settings.gomplate.timeout- timeout in seconds to execute Gomplate Datasources -
templates.settings.gomplate.datasources- a map of Gomplate Datasource definitions:-
The keys of the map are the datasource names, which are used in
Gotemplates in Atmos stack manifests. For example:terraform:
vars:
tags:
provisioned_by_ip: '{{ (datasource "ip").ip }}'
config1_tag: '{{ (datasource "config-1").tag }}'
config2_service_name: '{{ (datasource "config-2").service.name }}' -
The values of the map are the datasource definitions with the following schema:
-
url- the Datasource URL -
headers- a map of HTTP request headers for thehttpdatasource. The keys of the map are the header names. The values of the map are lists of values for the header.The following configuration will result in the
accept: application/jsonHTTP header being sent with the HTTP request to the datasource:headers:
accept:
- "application/json"
-
-
Some functions are present in both Sprig and Gomplate.
For example, the env function has the same name in Sprig and
Gomplate, but has different syntax and accept different number of arguments.
If you use the env function from one templating engine and enable both Sprig
and Gomplate, it will be invalid in the other templating engine, and an error will be thrown.
For this reason, you can use the templates.settings.sprig.enabled and templates.settings.gomplate.enabled settings to selectively
enable/disable the Sprig and Gomplate
functions.
Environment Variables
Most YAML settings can also be defined by environment variables. This is helpful while doing local development. For example,
setting ATMOS_STACKS_BASE_PATH to a path in /localhost to your local development folder, will enable you to rapidly iterate.
| Variable | YAML Path | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ATMOS_CLI_CONFIG_PATH | N/A | Where to find atmos.yaml. Path to a folder where atmos.yaml CLI config file is located (e.g. /config) |
| ATMOS_BASE_PATH | base_path | Base path to components and stacks folders |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_TERRAFORM_COMMAND | components.terraform.command | The executable to be called by atmos when running Terraform commands |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_TERRAFORM_BASE_PATH | components.terraform.base_path | Base path to Terraform components |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_TERRAFORM_APPLY_AUTO_APPROVE | components.terraform.apply_auto_approve | If set to true, auto-generate Terraform backend config files when executing atmos terraform commands |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_TERRAFORM_DEPLOY_RUN_INIT | components.terraform.deploy_run_init | Run terraform init when executing atmos terraform deploy command |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_TERRAFORM_INIT_RUN_RECONFIGURE | components.terraform.init_run_reconfigure | Run terraform init -reconfigure when executing atmos terraform commands |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_TERRAFORM_AUTO_GENERATE_BACKEND_FILE | components.terraform.auto_generate_backend_file | If set to true, auto-generate Terraform backend config files when executing atmos terraform commands |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_HELMFILE_COMMAND | components.helmfile.command | The executable to be called by atmos when running Helmfile commands |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_HELMFILE_BASE_PATH | components.helmfile.base_path | Path to helmfile components |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_HELMFILE_USE_EKS | components.helmfile.use_eks | If set to true, download kubeconfig from EKS by running aws eks update-kubeconfig command before executing atmos helmfile commands |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_HELMFILE_KUBECONFIG_PATH | components.helmfile.kubeconfig_path | Path to write the kubeconfig file when executing aws eks update-kubeconfig command |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_HELMFILE_HELM_AWS_PROFILE_PATTERN | components.helmfile.helm_aws_profile_pattern | Pattern for AWS profile to use when executing atmos helmfile commands |
| ATMOS_COMPONENTS_HELMFILE_CLUSTER_NAME_PATTERN | components.helmfile.cluster_name_pattern | Pattern for EKS cluster name to use when executing atmos helmfile commands |
| ATMOS_STACKS_BASE_PATH | stacks.base_path | Base path to Atmos stack manifests |
| ATMOS_STACKS_INCLUDED_PATHS | stacks.included_paths | List of paths to use as top-level stack manifests |
| ATMOS_STACKS_EXCLUDED_PATHS | stacks.excluded_paths | List of paths to not consider as top-level stacks |
| ATMOS_STACKS_NAME_PATTERN | stacks.name_pattern | Stack name pattern to use as Atmos stack names |
| ATMOS_STACKS_NAME_TEMPLATE | stacks.name_template | Stack name Golang template to use as Atmos stack names |
| ATMOS_WORKFLOWS_BASE_PATH | workflows.base_path | Base path to Atmos workflows |
| ATMOS_SCHEMAS_JSONSCHEMA_BASE_PATH | schemas.jsonschema.base_path | Base path to JSON schemas for component validation |
| ATMOS_SCHEMAS_OPA_BASE_PATH | schemas.opa.base_path | Base path to OPA policies for component validation |
| ATMOS_SCHEMAS_ATMOS_MANIFEST | schemas.atmos.manifest | Path to JSON Schema to validate Atmos stack manifests. For more details, refer to Atmos Manifest JSON Schema |
| ATMOS_LOGS_FILE | logs.file | The file to write Atmos logs to. Logs can be written to any file or any standard file descriptor, including /dev/stdout, /dev/stderr and /dev/null). If omitted, /dev/stdout will be used |
| ATMOS_LOGS_LEVEL | logs.level | Logs level. Supported log levels are Trace, Debug, Info, Warning, Off. If the log level is set to Off, Atmos will not log any messages (note that this does not prevent other tools like Terraform from logging) |
| ATMOS_SETTINGS_LIST_MERGE_STRATEGY | settings.list_merge_strategy | Specifies how lists are merged in Atmos stack manifests. The following strategies are supported: replace, append, merge |